
The outer mitochondrial membrane allows for the establishment of the intermembrane space. Overview of Respiration What is Cellular Respiration It is the process by which organisms use energy from food (e.g., glucose, fatty acids) to fuel the endergonic synthesis of ATP.We will outline the main adaptations of the mitochondria below: This double membrane structure creates five distinct components within the mitochondria, and each of these aids aerobic respiration in some way. The mitochondria have an inner membrane and an outer membrane. The link reaction, the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation all take place within the mitochondria.Īs displayed in Fugire 1, the mitochondria’s structural features help to explain its role in aerobic respiration.
Fermentation is the name given to many different types of anaerobic respiration, which are performed by. Eukaryotic organisms perform cellular respiration in their mitochondria organelles that are. requires (O 2), occurs in most organisms (plants, too) provides a supply of usable energy for cells (ATP) C 6 H 12 O 6 6HCO 2 2 OATPs Glucose Oxygen gas Carbon dioxide 6.

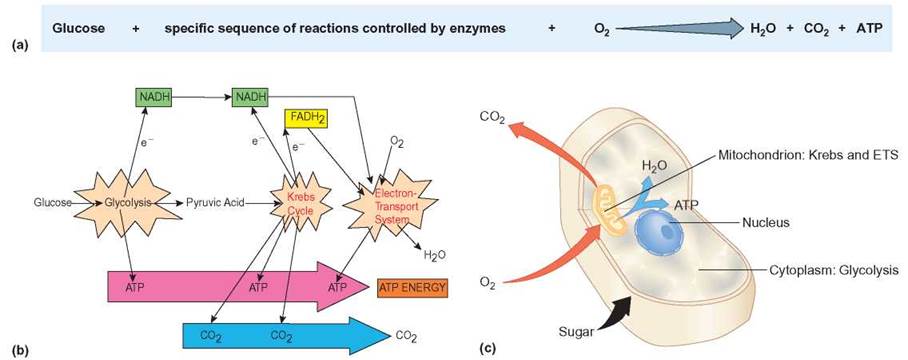
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, which is the liquid that surrounds the cell’s organelles. Types of Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration. What is Cellular Respiration It is the process by which organisms use energy from food (e.g., glucose, fatty acids) to fuel the endergonic synthesis of ATP. In animal cells, three of the four stages of aerobic respiration take place in the mitochondria. Where does aerobic respiration take place? Chapter 09 - Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Overview: Life Is Work Concept 9.1 Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels. It is different from anaerobic respiration, which does not require oxygen to occur and produces far less ATP. The key part of aerobic respiration is that it requires oxygen to occur. Glucose is known as a respiratory substrate, and is broken down by cells to produce energy in the form of ATP. Transcription and Translation in Prokaryotesĭuring aerobic respiration, ATP is generated from oxygen and glucose.Changes in Signal Transduction Pathways.Heterotrophs depend on autotrophs, either directly or indirectly. Humans are heterotrophs, as are all animals. Even if the food organism is another animal, this food traces its origins back to autotrophs and the process of photosynthesis. The Greek roots of the word heterotroph mean “other” ( hetero) “feeder” ( troph), meaning that their food comes from other organisms. Heterotrophs are organisms incapable of photosynthesis that must therefore obtain energy and carbon from food by consuming other organisms. Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidised in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor such as oxygen to produce large. Plants are also photoautotrophs, a type of autotroph that uses sunlight and carbon from carbon dioxide to synthesize chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates.

Oceanic algae contribute enormous quantities of food and oxygen to global food chains. Plants are the best-known autotrophs, but others exist, including certain types of bacteria and algae. The Greek roots of the word autotroph mean “self” ( auto) “feeder” ( troph). An autotroph is an organism that can produce its own food. Some organisms can make their own food, whereas others cannot.

When the covalent bond between the terminal phosphate group and the middle phosphate group breaks, energy is released which is used by the cells to do work. \): Chemical structure of ATP consists of a 5-carbon sugar (ribose) attached to a nitrogenous base (adenine) and three phosphates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
